Management¶
You can here see and manage the current units here. Also filter per family and/or label to quickly find the data.
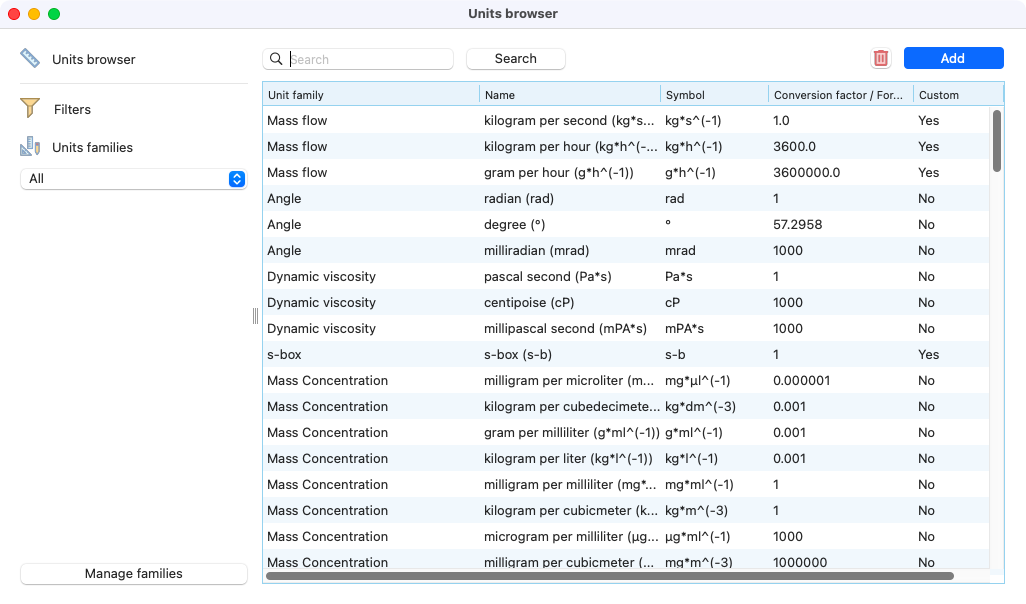
View of the units home page.¶
Warning
As usual, only units that are not used in Laby can be deleted.
Double click on a unit to open the details and modify if needed. Here is an example with the reference: the conversion factor is set to 1.
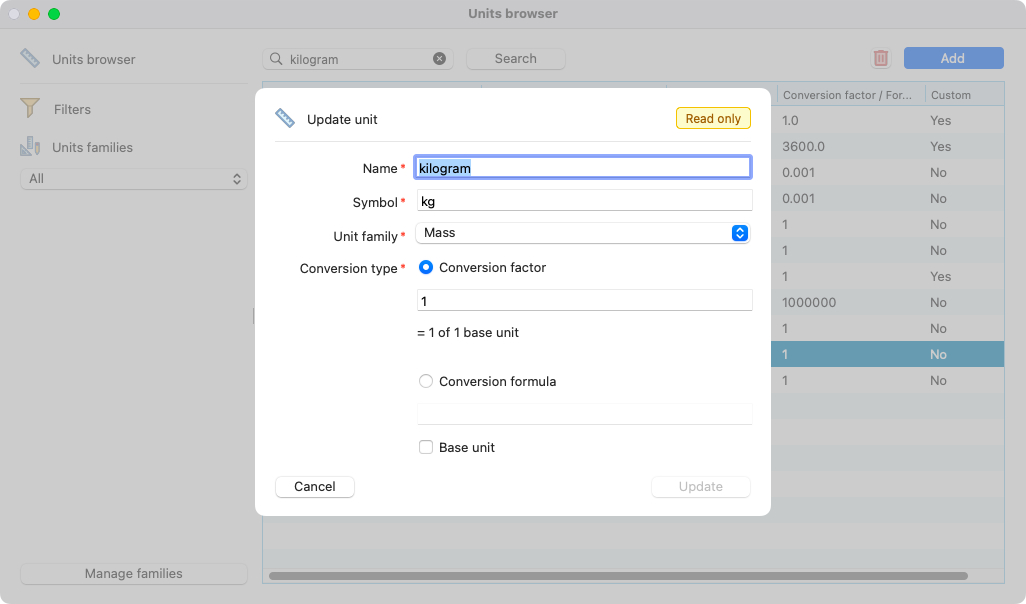
View of the unit kilogram open.¶
Warning
the conversion factor is used in the inventory management and is used to calculate the level of items and the value.
Here is an example with the unit gram, which 1000 units are equivalent to 1 kilogram. That means the conversion factor is 1000.
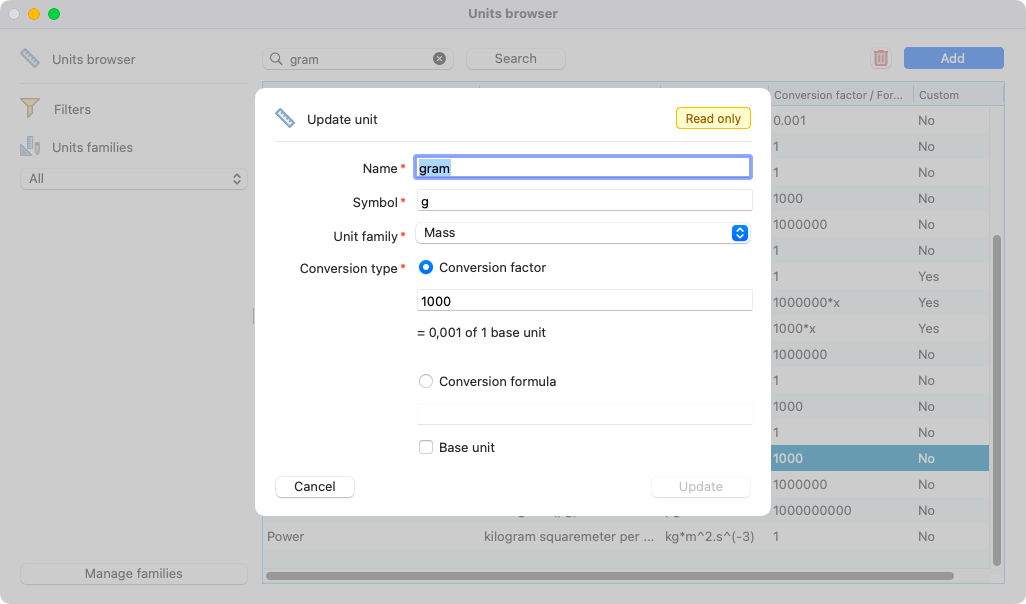
View of the unit gram open.¶
Note
Other examples of unit conversion:
- Mass:
kg = 1 → reference
g = 1000 → needs 1000g to have 1kg
t = 0,001 → needs 0,001 ton to have 1kg
- Period:
second = 1 → reference
minutes = 0,01666 (1/24) → 0,0166min to have 1s
milliseconds = 1000 → 1000ms to have 1s
- Unit:
unit = 1 → reference
box = 1 → can be same as reference
box 20 = 0,05 (1/20) → 20 units = 1 box
box 100 = 0,01 (1/100) → 100 units = 1 box
Manage Families¶
After clicking on the button manage families, it is possible to add, remove and edit families. Here is how it looks like the unit family browser:
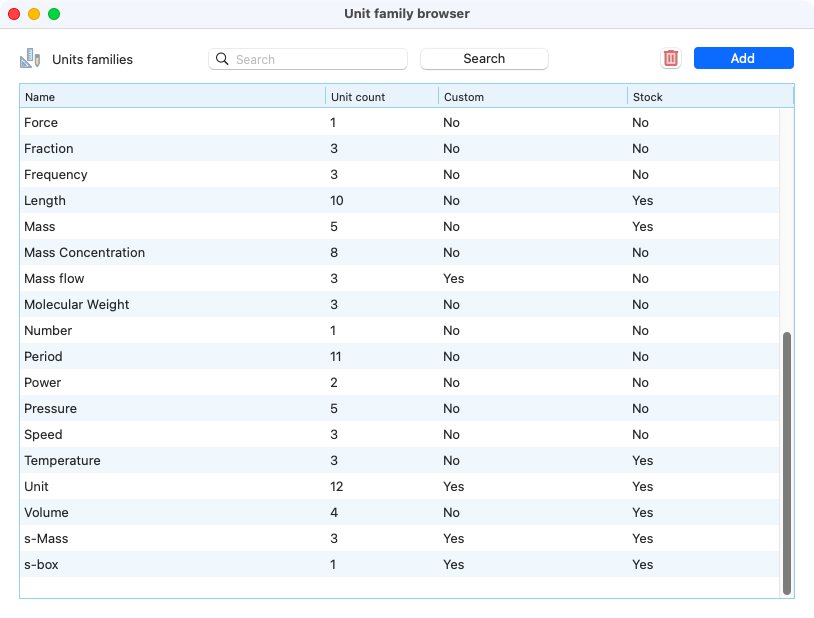
View of the unit family browser.¶
When you click on add a new unit family, you can define a name and select if it will appear to be used on stocks.
View when creating a new unit family.¶
Units management for the inventory¶
This unit management system aims to provide a real-time, complete view of stock levels, usage, and valuation. The system is designed to meet the needs of items used in lab experiments.
Key Parameters¶
Three key parameters define the granularity of inventory management:
Traceability: The need to track the batch or lot of the item used in experiments.
Stock Level Monitoring: Whether tracking should be done per box/packet or by mass/volume.
Valuation: For high-cost items, track each use to manage project costs and stock.
With Laby you can specify the unit you want to use to follow the usage and consumption of your items.
Warning
The unit of a product can not be modified after its creation
Examples¶
1: Antibodies
Traceability Requirement: High
Stock Monitoring: Per µL
Valuation Requirement: High
→ Stock units will be in volume/mass (µL/mL, mg/g etc.).
Inventory is updated by the defined quantity used in an experiment.
For instance, a shipment will be logged as 150µL x 2 (tubes).
2: 50 mL Falcon Tubes
Traceability Requirement: Low
Stock Monitoring: Per pack of 25
Valuation Requirement: Low
→ The stock unit will be in ‘unit/pack’.
Inventory is updated when a pack is taken out of the general stock.
For instance, a carton delivery containing 5 packs will be logged as 1 pack x 5.
3: High-Cost Syringes
Traceability Requirement: Average - High
Stock Monitoring: Per unit
Valuation Requirement: Important
- → The stock unit will correspond to the box containing 5 units (1 unit = 1 syringe).
Inventory is updated when one or more units are used in experiments.
A delivery will be logged as 5 units x 2 (boxes).
→ The flexible nature of this inventory management system makes it highly adaptable to various kinds of materials and requirements, providing a fine-tuned control over lab resources.