Introduction¶
In this section, we will discover:
The purpose of stucturing projects.
Each entity of a project structure:
Program.
Project.
Step.
Study.
Experiment.
Test.
The user guide to manage your project:
How to create a program.
How to create a project.
The common functions of the project hierarchy.
Special functions offered in order to maximise your experience.
Definition¶
The key to efficient research is to use knowledge, a quality-based system, and continuous improvement. With its deeply minded project structuration, Laby offers the easiest way to:
Organize a project.
Structure and retrieve information following the ALCOA++ principles.
Speed up new team member integration.
Improve learning curve.
Anticipate resources needs.
Distribute information for actuals vs budget and forecast comparison.
and more.
Laby contextualizes all the project-related information you consult! Through a single view and in a second, you can understand:
The way the project has been developed.
The finalized steps (milestones, work packages, etc.).
The ongoing activities.
The planned studies.
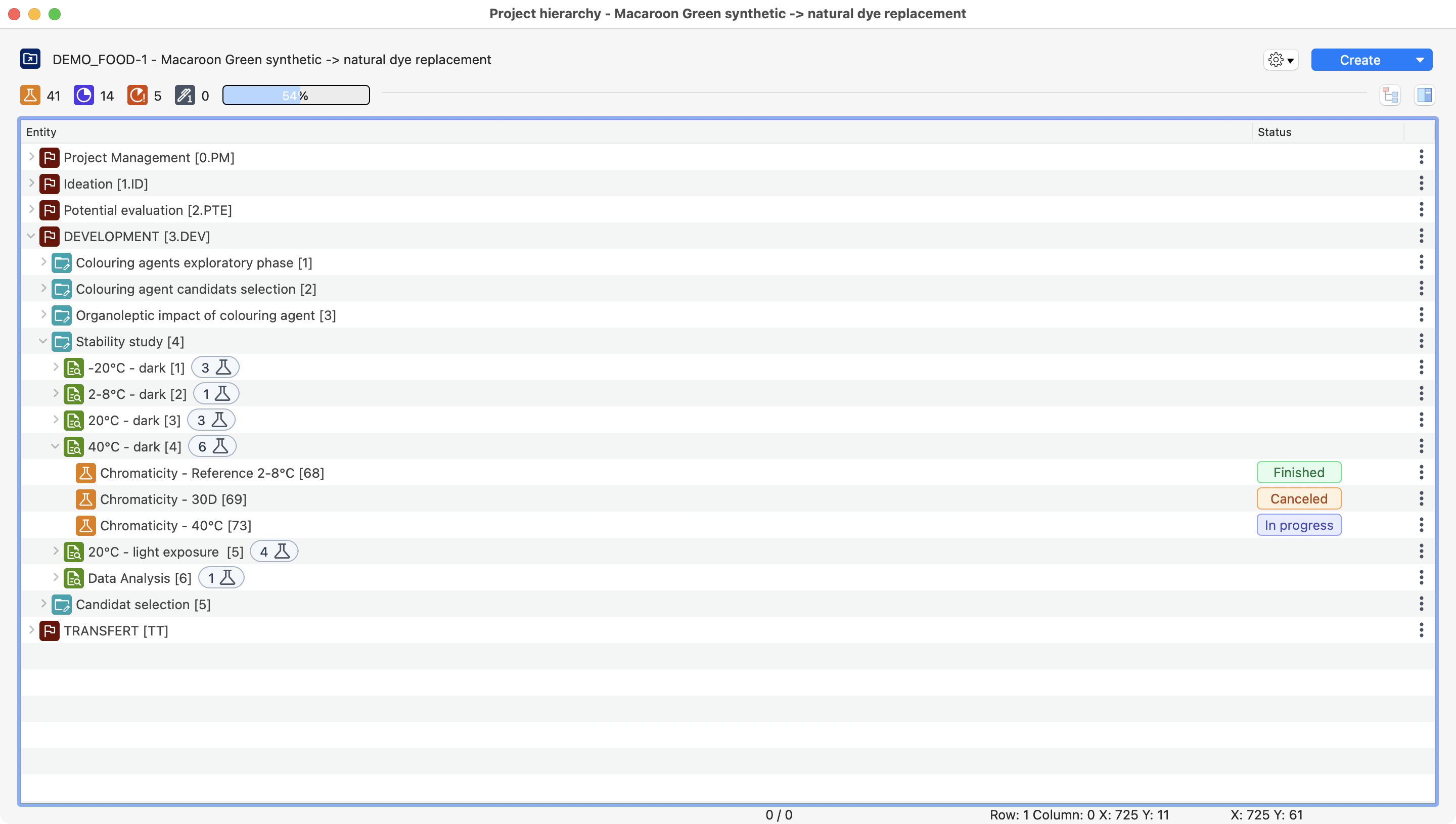
View of a project inside Laby. With steps, experiments, tests, and all its information.¶
Here is a short description of each level of the hierarchy and its purpose:
Entity |
Logo |
Codification |
Description |
Example |
Program |
XX-YYY |
Represents a collection of projects managed in a coordinated way to reach a strategic goal. May regroup projects around a specific research, partner, or business area. |
“Neuroscience Research 2021” |
|
Project |
01 |
Regroups all activities of specific projects. Usually defined by a target product profile or attached to a contract, budget, etc. |
“Alzheimer’s Drug Development” |
|
Step |
ZZ |
Regroups activities for a step or milestone of a project. It marks a big stage in the project’s development. It may lead to a Go/No-Go decision. It may also represent a work package for consortium projects. Transversal teams have access to related milestones. |
“Pre-Clinical Testing” |
|
Study |
00 |
Correlated to answer a point of the block of activities. Might represent development methods. These methods lead to a validation, calibration curves, or assessing product criteria. |
“API Solubility Analysis” |
|
Experiment |
11 |
Represents a set of tests to support, refute, or validate a hypothesis. Experiments provide insights into cause-and-effect. They show what happens when a factor is changed. Multiple experiments in a study may reflect iterations. |
“Solubility in Different Solutions” |
|
Test |
111 |
The lowest level in the hierarchy. Aims to collect results of an analysis. This includes the experimenter, protocol, date, raw material, and more. It processes data for human analysis. It also centralizes related information: raw data, videos, photos, and specific files. |
“Solubility in Saline Solution Test” |